Industrial Computer Vs Commercial Computer

Industrial PCs and commercial PCs are often being compared to one another in industrial computing applications. This is because they have similar computing capabilities in terms of storage, processing, and communications. However, industrial PCs are designed to have greater reliability, longevity, and flexibility . Here in this blog, we will guide you to uncover the differences between industrial PCs and commercial PCs and what makes the industrial computer a key solution in enterprise-level computing deployments.
What is A Commercial Computer?
A commercial computer is a term to describe a more intensive computing application that demands higher capabilities and reliabilities than normal consumer-grade products. Commonly placed in controlled indoor environments due to its huge size and high-power requirements. For example, a workstation computer is a commercial computer with higher computing performance than a personal computer but is less advanced than industrial computers. Both industrial and workstation computers have a high capacity for GPU interface and high-performance but are different in terms of their ruggedness. Common task commercial computer is used for:
- Access the internet
- Word processing software
- Rendering high-definition videos, musics and games
- Data analysis
What is An Industrial Computer?
Industrial computers are specifically engineered to work in remote industrial operations with harsh environments that require efficiency and reliable performances. What makes industrial computers special from other computers is their robust designs while maintaining high performance. Industrial computers run more complex tasks such as:
- Processing powerful automation software (robot automations)
- Data acquisition (predictive maintenance)
- High-precision machine vision
- Machine-to-machine (M2M) communications
- AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle) Systems
Industrial Computers Vs Commercial Computers
There are significant differences between industrial and commercial computers. Many of the differences are related to its ability for continuous operation in harsh environments that can cause detrimental failures. For example, industrial computers are robust in mechanical structure design and use fanless and cable-less designs . These key design features are specifically designed into the industrial computer to ensure durability, reliability, and longevity when exposed to the harshest environments that are susceptible to water, dust, extreme temperature, shock, and vibration.
Designs and Components
1. Fanless Vs. Fan-cooled
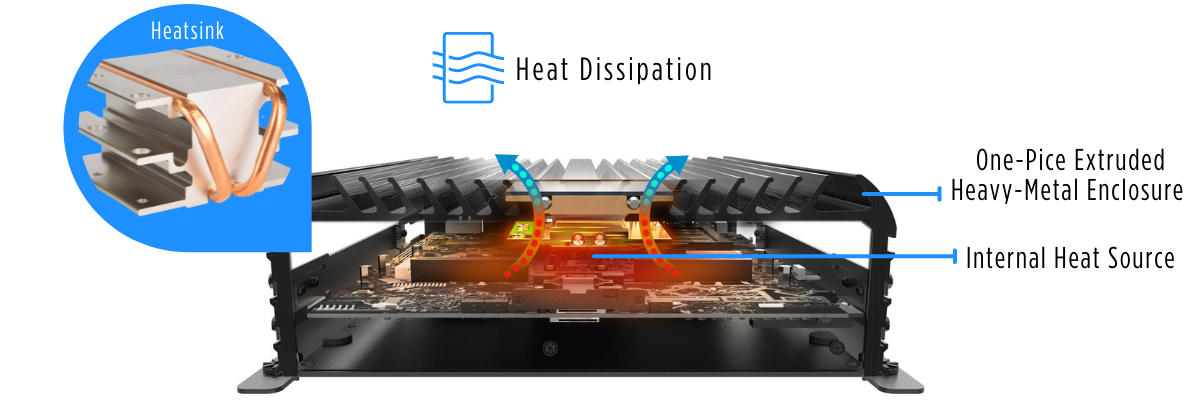
Industrial computers are known for their unique and fanless design. Instead of using an active spinning fan for fan cooling, industrial computers utilize heatsinks and heat pipes to dissipate the heat from the hottest part of the computer (CPU) up to the outer portion of the computer. It is a very simple yet effective method in removing heat from critical components to ensure a computer continues to operate. In contrast, many commercial computers use active cooling methods fan-cooled transformers to dissipate heat, something not suitable for industrial applications.
Learn more about Fanless Computer Designs and How They Work
2. Cableless Vs. Cabled
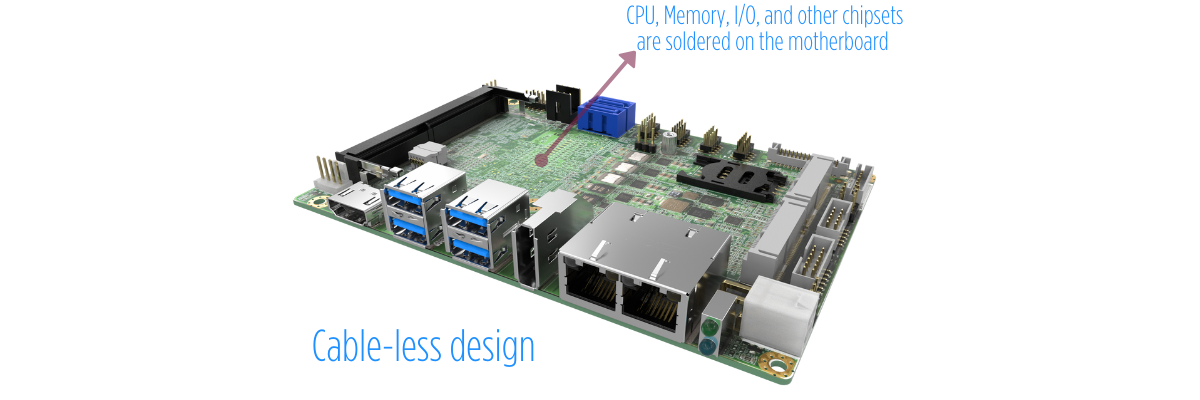
Industrial computers eliminate cable usage to reduce the possibilities of loose cables from their connection, withstand external interruption, and cable burned out. Instead, they maximize the use of hot-swappable expansion cards to connect each of the components. While for commercial computers, the reason why they tend to stay in a controlled environment is also because of their cabled computer components.
3. Industrial grade Vs. Commercial-Grade Components
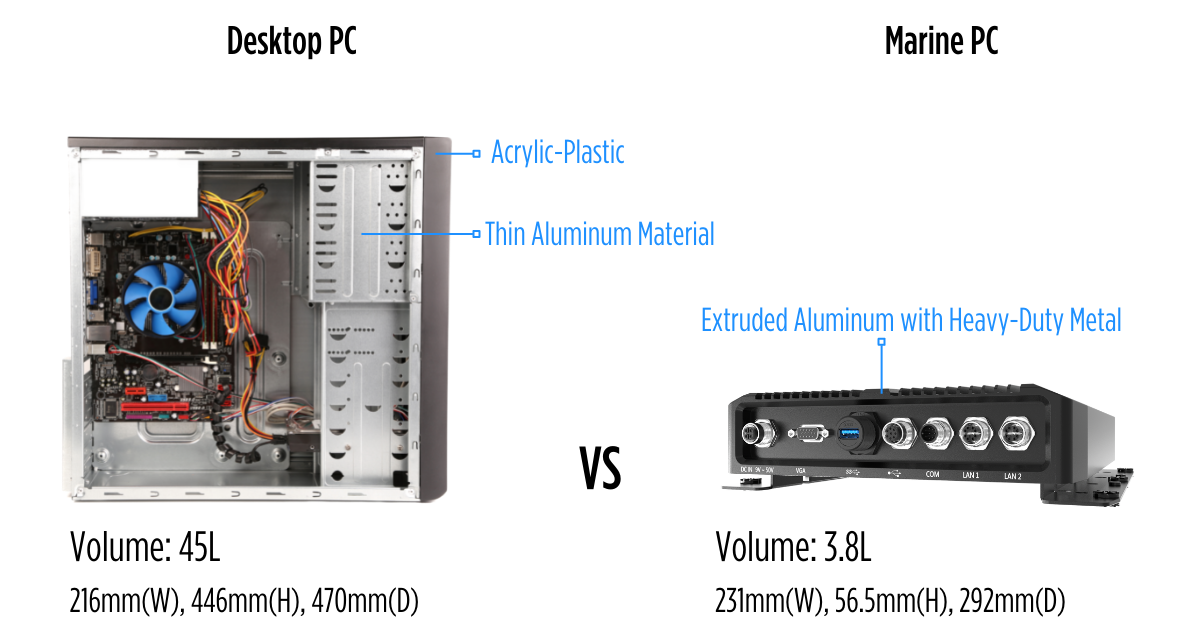
Industrial computers are made from industrial-grade materials tested to ensure durability and reliability when deployed in harsh environments. Unlike commercial computers that have not been designed to survive harsh environments, industrial computers use high-quality components that have been tested to endure wide-operating temperatures. For example, industrial-grade computers chassis are made out of extruded heavy-duty metal to survive tough industrial challenges such as shock and vibration. In contrast, a commercial computer's chassis is often time made out of thin aluminum and acrylic plastic to keep costs down.
Ruggedness and Reliability
1. Shock and vibration
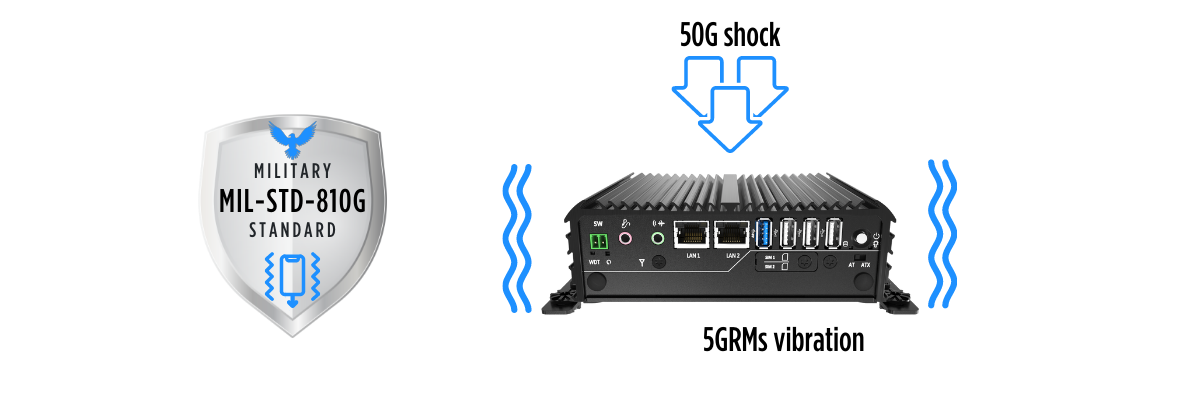
Industrial applications like robotic automation and mining processes often encounter a high level of shock and vibration. Therefore, industrial computers are designed in a way to limit the potential failure caused by shock and vibrations. In order to ensure reliability, under these conditions, the best industrial computers eliminate failure points by incorporating fanless designs and using a one-piece chassis. The exterior shell is specifically built in a one-piece design to avoid additional joints and screws. These industrial-grade design techniques provide a robust structure that can even meet MIL-STD-810G qualifications in shock and vibration, which indicates a computer's ability to be used in specific military applications.
On the other hand, commercial computers consist of many moving parts, such as cables, fans, and hard disks. The exterior chassis is made up of aluminum metal and acrylic plastic, which are not designed to withstand high levels of shock and vibrations. In fact, many aspects of a commercial computer are not suitable for shock and vibration because of common failure points.
Learn more about Vibration Resistant Embedded Computer
2. IP (Ingress Protection) rating
The key for rugged and reliable industrial computers is eliminating multiple failures, especially from dust and water elements. Many industrial applications require the computer to function in extremely dirty and water-logged environments; for example, automation equipment in food processing requires daily hygienic washdowns with high-power jets with special chemical agents. Therefore, industrial computers are accompanied by the level of IP protection from the exterior design (one-piece chassis), fanless cooling, and even special connectors (M12) to keep out dust and water. M12 Connectors are dust and water-proof connectors, with a built-in locks in order to secure cables to a computing machine. At the same time, the fanless designs avoid the inflow of dust and foreign particles into the computer's components because of the removal for ventilation holes that are required with active fan cooling.
Commercial computers and their use cases often times do not require IP rating. But since most commercial computers are used indoors and in dry office spaces, there is no need for IP protections.
Learn more about IP67 Embedded Systems | Tightly Sealed Waterproof and Dustproof Indust
3. Extreme temperatures

As mentioned before, an industrial pc utilizes a heatsink and heat pipe instead of using a fan to dissipate the heat effectively. It is also assembled from highly durable industrial-grade components that can handle a higher temperature ranging from –40⁰C up to 85⁰C, enabling operation in extreme cold and hot environments.
Commercial computers with active cooling fans can only withstand temperatures that range from 0 ⁰C –35⁰C. Heat is a detrimental element for computing electronics because it can damage mission-critical components like the CPU, memory, and storage if not properly cooled. Therefore, active fans are popular cooling solutions for commercial computers to remove heat from the system itself.
Learn more about Wide Temperature Range Embedded Systems
4. Electromagnetic interference (EMI)
Electromagnetic interference is a phenomenon where one electromagnetic field interferes with another in the same range of radiofrequency (RF). EMI causes degradation of the circuit and may even stop it from functioning. Industrial computer designs ensure complete isolation and prevention from the radiation from penetrating through the computer. Compliance standards like FCC and EC are common practices to ensure EMI safety and compatibility. Both industrial computers and commercial computers must meet EMI compliance and safety regulation in order to be used in a variety of applications.
5. Wide power range

Industrial computer's power supply unit (PSU) design is completely fanless, cable-less, and wide voltage protection. The wide power range allows input ranging from 9V to 48V, accompanied by over-voltage protection (OVP) to prevent input of more than 55V and an overcurrent protection (OCP) to prevent inrush current from damaging the system. However, the commercial computer's PSU uses an active cooling fan and cables, causing the dust and dirt to clog up the system. A bad PSU causes fire from overheating and voltage fluctuations, leading to permanent damage to the computer's components.
6. Expansion capabilities, rich I/O ports Vs. Limited I/O ports
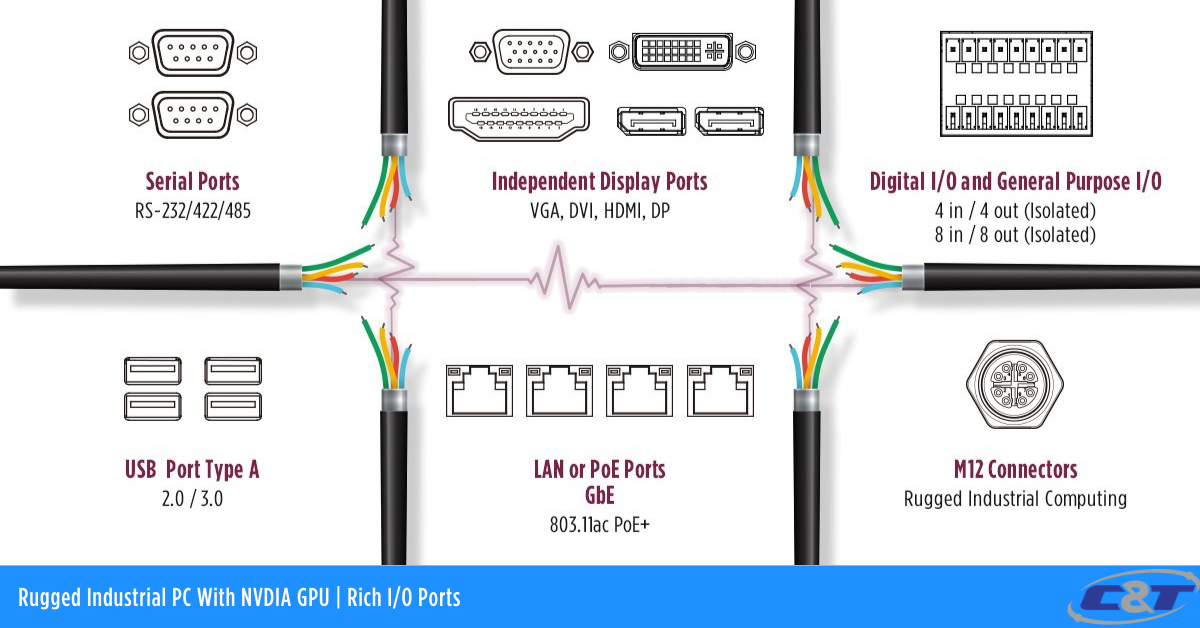
Industrial computers are capable of managing various data inputs that transmit data for real-time decision-making. In addition, industrial computers provide an extensive range of input/output ports to enable their expandability and capability in fulfilling industrial workloads. For example, there are serial ports, USB, PoE LAN, Video ports, DIO/GPIO, M12 ports, and much more. I/O flexibility is a key requirement for many industrial computing deployments that rely on both analog and digital connections. In contrast, commercial computers are limited in I/O but often times offer the latest in I/O ports for the best performance.
When Reliability Counts, Choose Industrial Computers
Industrial computers support embedded applications and can be used for 5 to 7 years due to their longevity in design. Overall, industrial computers are purpose-built for ultimate reliability and long-term use without any interruptions. As for commercial computers, their designs are based on the current trends that follow the performance as its requirement for specifications. That is why most commercial computers can be upgraded to the latest technology relatively quickly.
Commercial and Industrial Applications:
Commercial computer
Commercial and industrial computers have the same capabilities that work efficiently in different environments. However, commercial computer features active cooling fans and cable designs require them to work in a controlled room where dust and foreign particles are less likely to interfere with the computer's performance. For example:
- Office environment
- School environment
- Every-day use computer
Industrial computer
1. Manufacturing and industrial automation
Industrial computers manage motion control systems for product inspection, data logging, and data analysis for improved manufacturing productivity. For example, industrial computers have increased the accuracy and efficiency of computer industry operations, usually used to automate various processes involved in motherboard PCB making.
2. Interactive kiosk
Kiosk machines are everywhere; small industrial fanless PCs power all self-service kiosks since they are compact and pretty powerful to run various kiosk applications. Mini industrial PCs improve multiple aspects of our life by delivering a seamless experience. For example, integrating small form factor industrial PCs in a self-service kiosk in the airport enable passengers to eliminate the time spent waiting in a long queue during airport check-ins. Moreover, industrial computers are equipped with high-speed ports like USB 2.0 and 3.0 to provide enormous flexibility and power many IoT sensors integrated into kiosk machines for self-service automation.
3. Automation inspection and testing equipment
Quality control applications need the combination of machine vision or digital measurement instruments in order to process information with speed and accuracy. Industrial computers with GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) enable the system to run machine inferencing at the edge without being dependent on the cloud. Industrial computers with GPUs enable the machine to perform intelligent machine vision, which ensures all measurements are precise and components are manufactured according to predetermined specifications., Industrial PCs also help speed up the manufacturing process with greater accuracy and intelligence by running automation software for flexibility.
4. Security and surveillance
Security and surveillance solutions are often placed in harsh environments, like public transportation systems and outdoor security systems. Industrial PCs are capable of withstanding deployments in tough environments; Moreover, some industrial computers are specialized with multiple PoE ports that provide stable connections to IP cameras. Moreover, PoE allows industrial computers to deliver power and transmit video footage data on a single cable. Thus, reducing the cabling footprint of the security system while improving passenger's safety.
5. Underground mining
Underground mining requires computers to withstand the demanding conditions of dust, wide temperature range, shock, and vibrations. Industrial computers are perfectly made for this operation. Known for their robust structure, highly critical performance, and accuracy in capturing valuable telemetry for construction and digging sites, industrial computers can quickly be deployed at a remote underground site for processing and data telemetry.
6. Military and maritime
Industrial computers are capable of surviving the harsh operating conditions of ground control operations and aboard ships in the maritime industry. They require low maintenance and long operating life that meets the MIL-STD-810G qualification in shock and vibration. Most importantly, industrial computers are engineered to be fully dust and water-resistant to operate in various military applications.

What Makes Up the Best Industrial PC?
Industrial PCs are designed and assembled to fit into industrial applications with proven reliability. Its One-piece chassis design and fanless cooling protect the computer from external debris intrusion and wide temperature environments. In addition, industrial PCs can also provide IP ratings to ensure their resistance against water ingress and dust particles. Last but not least, industrial PCs provide a wide range of input/output ports for expansion capability, making it easier to upgrade and replace parts of computers.
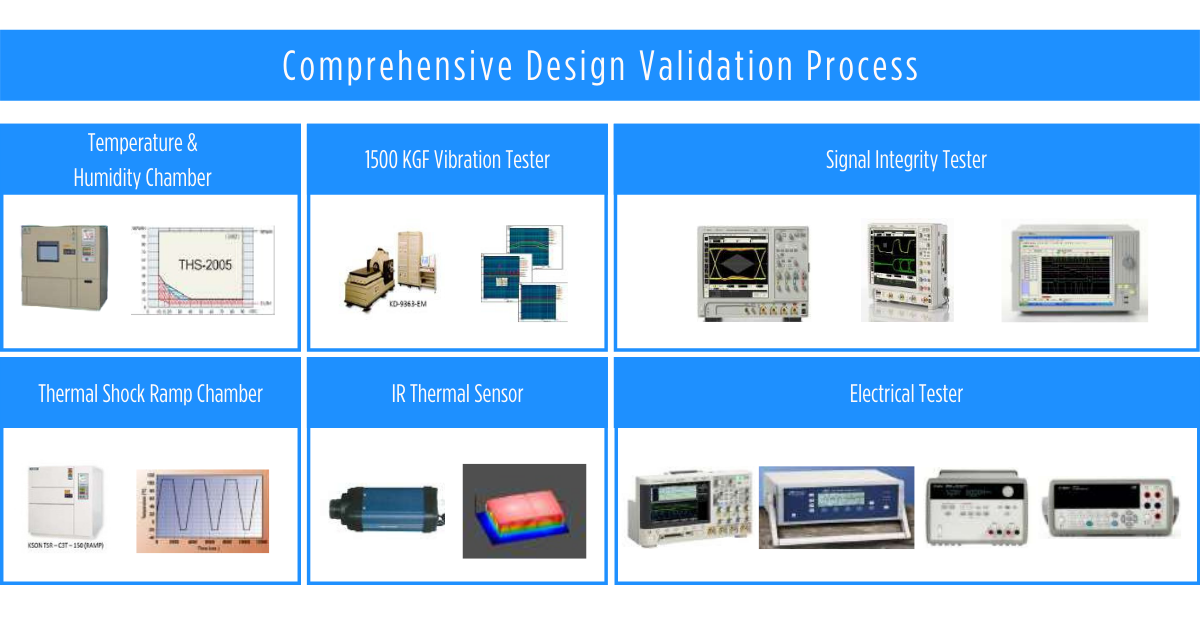
Industrial Computer Test and Validation process
Industrial computer manufacturers implement a comprehensive design validation process in order to ensure reliability. The purpose of a thorough design qualification process is to ensure durability, reliability, and longevity of the product in design. Dedicated testing and specification measurements are held in reliable testing facilities with specialized equipment such as temperature & humidity chamber, 1500 KGF vibration tester, thermal shock ramp chamber, IR thermal sensor, signal integrity tester, and electrical tester. These tests include:
- Compliance test: Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) test for EC and FCC certifications.
- Signal Measurement: Signal integrity for high-speed peripherals to ensure best design attributes
- Stress Test: Observe results when operating beyond the normal standard or meeting maximum specification
- Functional Test: Basic I/O functional test, boot up test, OS, power protection, power consumption, performance test, full loading test
- BIOS setup test: To ensure the system properly, configures settings, and initializes all functions and devices
- Compatibility test: To ensure CPUs, DIMMs, display cards, and other peripherals are compatible with the system
- Environmental Test: Thermal test including four corners, operating and non-operating, booting test, shock & vibration test, sealing for IP rating, and thermal shock test
Why C&T?
C&T designs high-quality industrial-grade PCs and has been recognized for its robust designs and outstanding performances. C&T has successfully evolved into a full-service technology company specializing in top-notch computing designs that help customers overcome the greatest challenge in industrial applications. That being said, visit "contact us" to talk with one of our technical experts to discover the best industrial computing solutions that meet the requirements of your unique industrial application.


